Clustering
Spring Boot Admin Server supports cluster replication via Hazelcast. It is automatically enabled when a HazelcastConfig- or HazelcastInstance-Bean is present.
You can also configure the Hazelcast instance to be persistent, to keep the status over restarts. Also have a look at the Spring Boot support for Hazelcast.
When using clustering, Spring Boot Admin Events and Notifications are replicated across the members in the cluster. The applications are not replicated, each instance of Spring Boot Admin will have its own set of applications. This means that each instance has to monitor all applications, which may lead to increased load on the monitored services. Otherwise, you would have to ensure that each application is only monitored by one instance of Spring Boot Admin.
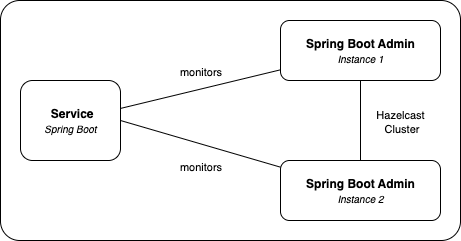
In the setup shown in the picture above, both Spring Boot Admin instances poll the monitored services for health checks. This means each service receives health check requests from every SBA node in the cluster.
Example Configuration
The following example shows a simple Hazelcast configuration, which should work in most environments. It uses multicast for discovery, which may not be available in all networks and does not require a dedicated Hazelcast server. All instances (aka members) of the Spring Boot Admin Server when using this config, will form a cluster automatically.
Keep in mind that Hazelcast has a lot of options to configure the network and discovery. Please refer to the Hazelcast Documentation for more details, as we do not offer any kind of support for Hazelcast itself. Also, this is just a basic example, you should adapt the configuration to your needs, especially regarding production readiness and network configuration.
- Add Hazelcast to your dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.hazelcast</groupId>
<artifactId>hazelcast</artifactId>
</dependency>
- Instantiate a HazelcastConfig:
@Bean
public Config hazelcastConfig() {
// This map is used to store the events.
// It should be configured to reliably hold all the data,
// Spring Boot Admin will compact the events, if there are too many
MapConfig eventStoreMap = new MapConfig(DEFAULT_NAME_EVENT_STORE_MAP).setInMemoryFormat(InMemoryFormat.OBJECT)
.setBackupCount(1)
.setMergePolicyConfig(new MergePolicyConfig(PutIfAbsentMergePolicy.class.getName(), 100));
// This map is used to deduplicate the notifications.
// If data in this map gets lost it should not be a big issue as it will atmost
// lead to
// the same notification to be sent by multiple instances
MapConfig sentNotificationsMap = new MapConfig(DEFAULT_NAME_SENT_NOTIFICATIONS_MAP)
.setInMemoryFormat(InMemoryFormat.OBJECT)
.setBackupCount(1)
.setEvictionConfig(
new EvictionConfig().setEvictionPolicy(EvictionPolicy.LRU).setMaxSizePolicy(MaxSizePolicy.PER_NODE))
.setMergePolicyConfig(new MergePolicyConfig(PutIfAbsentMergePolicy.class.getName(), 100));
Config config = new Config();
config.addMapConfig(eventStoreMap);
config.addMapConfig(sentNotificationsMap);
config.setProperty("hazelcast.jmx", "true");
// network and join configuration (simple defaults good for local/dev)
NetworkConfig network = config.getNetworkConfig();
network.setPort(5701).setPortAutoIncrement(true);
JoinConfig join = network.getJoin();
join.getMulticastConfig().setEnabled(true);
return config;
}
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
spring.boot.admin.hazelcast.enabled | Enable Hazelcast support.
|
spring.boot.admin.hazelcast.event-store | Name of backing Hazelcast-Map for storing the instance events.
|
spring.boot.admin.hazelcast.sent-notifications | Name of backing Hazelcast-Map for storing the sent notifications.
|